
Sometimes it is necessary to figure out the average odds from a set of betting odds which can then be used as the basis for further calculations. For example, computing deviation and variance.
When using odds in European format (decimal) you can be forgiven for thinking that average betting odds are simply computed by building the arithmetic mean of the data to be analysed. Unfortunately, this is the wrong approach and leads to a deceptive result.
 Image: Elnur (Shutterstock)
Image: Elnur (Shutterstock)As a reminder, European odds are calculated as the reciprocal of the statistical probabilities of each event:
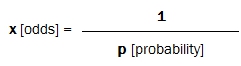
and vice versa … The implied probabilities are the reciprocals of the odds:
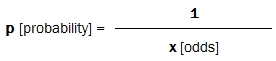
In effect, European odds are ratios/relations representing the likelihood of an event happening in comparison to each other event (e.g. a bet priced at odds of 4.0 is half as likely to win as a bet with odds of 2.0).
If these ratios are averaged using arithmetic mean (a common error), high data points are given greater weights than low data points. (e.g. working out the arithmetic mean of a set of 20 odds, 19 of them between 2.0 and 2.4, would be skewed if the 20th figure was, say, 15.0).
The correct approach is to calculate average odds by forming the harmonic mean!
The harmonic mean is defined as the reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of the reciprocals of x1, x2, …, xn (the odds):
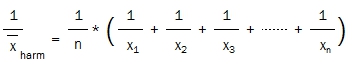
As the reciprocals of betting odds are the implied probabilities of the events, one can calculate the harmonic mean as a reciprocal of the average probability of the respective bets:
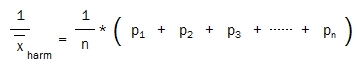
The above equations rearranged facilitates the harmonic mean calculation by dividing n (the number of matches) by the sum of the reciprocals of the odds:
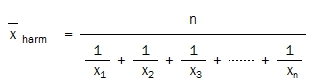
Or alternatively… dividing n (the number of matches) by the sum of their individual probabilities:
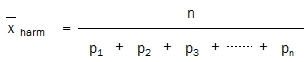
The Result (Harmonic Mean) is the Accurate Average of the Betting Odds.
Excel users employ the following formula: =HARMEAN(number1,number2,…)




Came across the article here whilst browsing – informative, even for a maths person like myself. My question is: what does harmonic mean GIVE us? Is it the ‘average’ odds per match, whose common value would give us the same returns as the originals? I have been playing with a spreadsheet, using only 3 values (3/1, 2/5 and 9/4 (aka 4.00, 1.4 and 3.25)) which gives a HM of 2.3585, but I can’t make the formulae work to give me the same returns as the calcs using the original values individually as an accumulator. Any possibility of a worked example? Regards A
Hello Soccerwidow!
Can you tell me please, how are the Asian Handicap markets calculated?
Thanks,
Hi sarkec, ASH calculation is going to be a whole course, much more massive than the OU course. It’s a very tricky calculation. Cannot be explained in few words. Sorry.
Hi,
When averaging the two zero odds for a home and away team in your over/under course, you use the arithmetic mean rather than the harmonic mean. In your example of U4.5 in the Wolfsburg v Bayern match the numbers are 1.16 & 1.24 so both averages come out quite close to 1.2
However, looking at U 2.5 in the same tables, using odds of 2 & 3 you get a arithmetic avg of 2.5 and harmonic of 2.4 which could potentially alter a decision as to value in the bet.
Could you please confirm which is correct and why?
Many thanks!
Hi Aussiebettor, I think you found an error in the course which needs to be amended. Using the harmonic mean for building average odds is correct.
Anyway, the course is due for review, and I will attend to it.
Very interesting article indeed. Would you use harmonic mean average if you we’re say calculating the average shots or corners taken by a given team over the season ?
Shots and corners are countable variables; they can be sorted into a natural order and possess a zero point. Therefore, these variables belong to the ratio scale, and for calculating of the average the ‘normal’ average mean is being used. Harmonic and geometric mean are pretty meaningless for this kind of variables.
You may find this article useful: Correct Assignment of Football Data to Levels of Measurement
Hi Soccerwidow,
Do you have any idea of how the over/under of a soccer match is priced please?
I do not think that it is automatically extracted from the 1×2 right ?
Thanks in advance.
Hi Betevo, correct, over/under odds are NOT automatically extracted from the 1X2 market.
You may be interested in my course on Over/Under odds calculation: Soccerwidow’s Football Betting Course – How to Calculate Odds: Betting on Over / Under ‘X’ Goals
Hi there,
Anyone that know where to find the following Calculator:
1) giving input in the form of odd for Over / under 2,5 & the odd for 1,X,2 outcome.
Giving estimated fair odd for ALL result from 0-0 to 9-9,
Thanks in the advance
Hi Goran,
it’s unfortunately not that easy.
However, here is a link to a calculator which will give you some probabilities if you put in the goal averages home & away: http://www.winnergambling.com/sports-betting-bingo/correct-score-betting-alculator/
Thanks for the link, Soccerwidow; unfortunatelly, it seems to be just simple Poisson distribution, that could be easily done in Excel as well, and is known as not really accurate, so nothing special…
Very interesting. Could one also use a geometric mean? My school maths is rusty but doesn’t a geometric mean provide a “typical value”, while a harmonic mean leans towards smaller figures in the set at the expense of larger ones?
The geometric mean is used for describing proportional growth, e.g. in business the geometric mean of growth rates is known as the compound annual growth rate (CAGR). In betting, the geometric means calculates the growth rate of success (profits/losses).
I’m in the process of writing an educational paper on this so keep looking…